Investigations: blood tests and imaging
Clinicians combine symptoms, examination, labs, and imaging to identify inflammation, obstruction, infection, or pancreatitis.
Common blood tests
| Test | Why it matters |
|---|---|
| LFTs (ALT/AST, ALP, GGT) | Patterns can suggest bile duct obstruction vs liver inflammation. |
| Bilirubin | Often rises with bile duct obstruction or cholangitis. |
| CRP | Inflammation marker; can rise in cholecystitis and infection. |
| FBC | White cell count may increase with infection/inflammation. |
| Lipase / Amylase | Elevated in pancreatitis (lipase preferred in many systems). |
| Electrolytes & renal function | Hydration, kidney status, and peri‑operative safety. |
| Albumin | Nutritional/inflammatory context; illness severity. |
| Clotting (INR/PT) | Bleeding risk and liver synthetic function; important pre‑op. |
Imaging
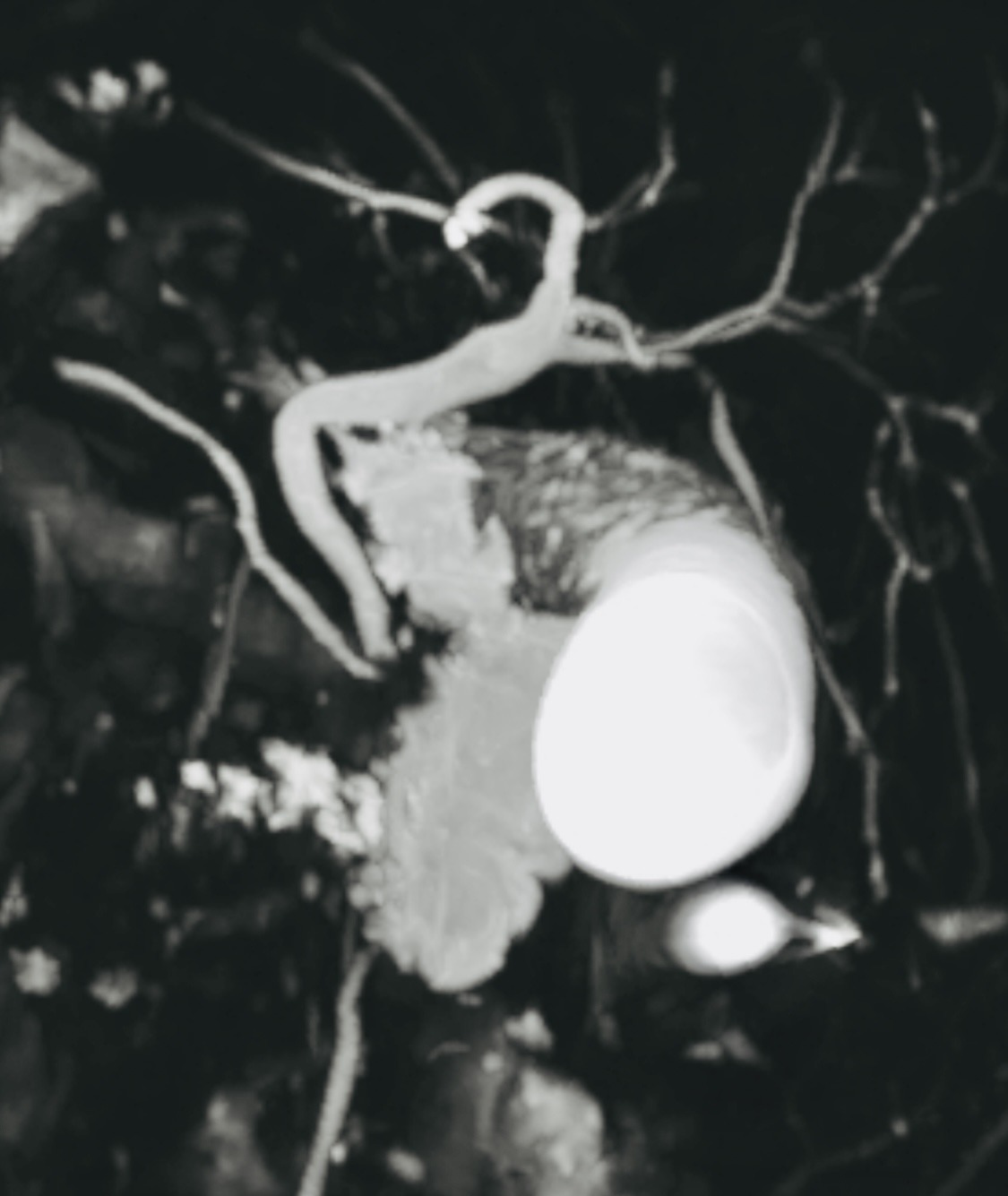
MRCP (a specialised MRI) can show the bile ducts and help detect a stone in the common bile duct. Image is illustrative.
When MRCP is helpful
- Jaundice or rising bilirubin/ALP/GGT
- Ultrasound suggests a dilated bile duct
- Concern for a stone in the common bile duct (choledocholithiasis)
- To guide whether ERCP is needed
Ultrasound (first line)
- Detects gallstones and sludge
- Looks for gallbladder wall thickening and fluid
- Assesses bile duct dilation
- Fast, no radiation
MRCP
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography is a specialised MRI sequence to visualise the bile ducts. It is typically used when bile duct stones are suspected but not confirmed.
Example: MRCP view of bile ducts (illustrative)
When MRCP is typically considered
- Jaundice or cholestatic pattern LFTs
- Ultrasound shows ductal dilation
- Concern for retained or migrating bile duct stones
Local protocols vary; clinicians weigh urgency and availability.
ERCP (when indicated)
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography can remove bile duct stones and relieve obstruction. Because it carries risks (including pancreatitis), it is usually used when treatment is needed, not just to “look”.
Practical point
Ultrasound is the usual starting point. MRCP and ERCP are reserved for suspected bile duct stones or complications.